Review: Interactions between Arenas
The Expected Pattern
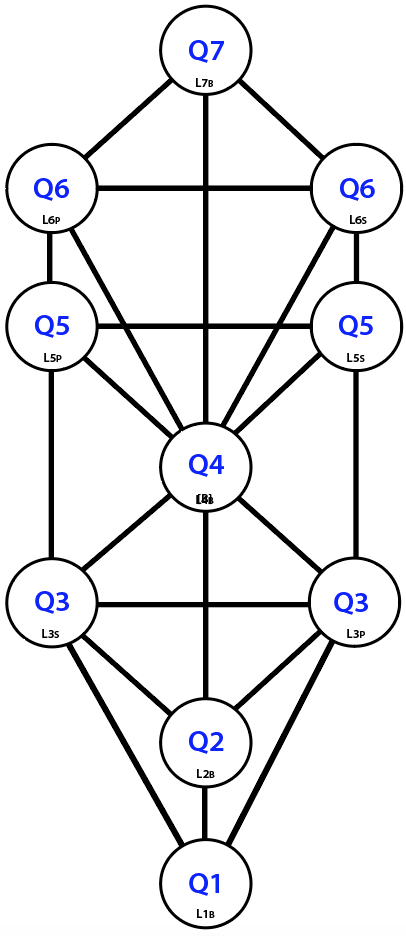
In the Architecture Room investigation of the Q-expansions, influences between the Arenas in a Domain were expected based on the overlap of adjacent arenas.
Each Domain Q-Tree viewed each of its Q1 to Q7 Arenas as Levels of a Tree with no re-ordering. Click on the thumbnail to see.
The primary psychosocial pressure of each Q-Arena in the Domain then aligned directly with the psychosocial pressure associated with levels within any Tree structure.
In the Domains studied then, it was not difficult to identify a dynamic social-personal duality in , and , and to be confident that no duality was present in , , and .
This then led to identification of an internal duality and an appropriate name for the Tree framework.
This approach will now be applied to the
Dynamic Duality
Polarization can be identified at the expected levels:
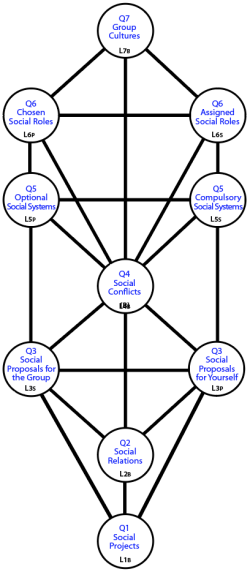
-
L3-Q3: can be developed by you , which will have a lesser or greater impact on the group; or they can be developed by you , which will have a lesser or greater impact on yourself.
Your will be dominant.
-
L5-Q5: can be with your involvement being fully socially) controlled using laws (e.g. the taxation system), or they can be where involvement is under personal control (e.g. the housing system).
The will be dominant.
-
L6-Q6: can either be , in which case what your fitting in is under external control, or they can be in which case you have control over fitting in.
The will be dominant.
By contrast:
-
L1-Q1: Any is simultaneously under personal control because joining is optional, while also being under social control because projects are developed and sustained by others.
-
L2-Q2: Any is simultaneously under personal control because the other person is your instrument, and also under control of the milieu which determines who this other person will be.
-
L4-Q4: Any is simultaneously under your personal control because you have to navigate it and decide your side, while also being under the control of the milieu that creates the divisiveness.
-
L7-Q7: A is simultaneously under your personal control because you have to assimilate to it while also being under social control because it is the group that creates the culture.
Implications
Internal Duality
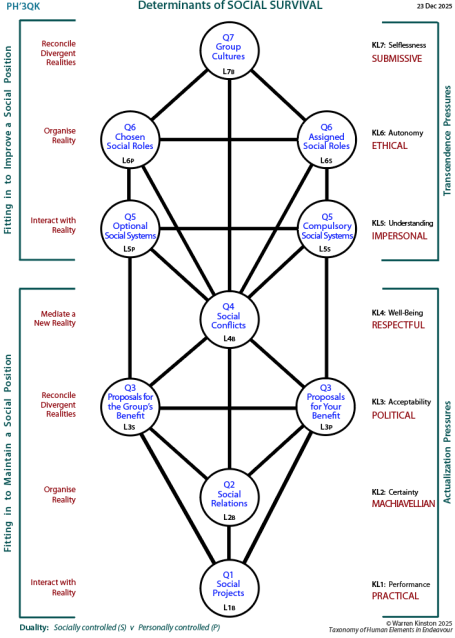
A clearer understanding of the Arenas' relations to each other emerges from considering the way their necessary "spirit" alters.
The diagram at right shows the spirit next to the standard psychosocial pressure of the level. There is the usual division into Transcendence (L5-L7) and Actualization (L1-L4) levels and the spirit quality aligns with that division.
These Arenas are omnipresent in society and a fact of life for everyone living in that society. Fitting in to groups is essential for psychological and even physical survival. So this Tree is provisionally named: .
The survival reference here is to the individual.
The internal duality suggested is:
«fitting in to maintain a social position» L's1-4
which corresponds to the actualization pressures
vs
«fitting in to improve a social position» L's 5-7
which corresponds to the transcendental pressures.
The Centre at the Heart
The standard pattern for reality interaction identified for all self-centred Trees is provided. It seems particularly significant that "mediating a new reality" aligns with the . Because all groups are formed around a shared reality, nothing divides a group more than the assertion of two realities: the old and the new in this case.
The larger the group the more likely there will be divisions and the largest group is a whole society. So the Tree is potentially also about survival of a society, which has unavoidable social divisions—ideological, racial, religious, geographical. If these are not addressed in a respectful spirit, then the society potentially faces a break-up.
Oscillation
If fitting in is a primal need, then it is a survival issue and cannot be ignored. Anyone who experiences the social milieu as failing to suit their nature and preferences must find and support a social environment somewhere that is more congenial.
George Bernard Shaw noted that "the reasonable man adapts himself to the world (i.e. fits in); the unreasonable one persists to adapt the world to himself. Therefore all progress depends on the unreasonable man."
In relation to the more focused Q-Arenas, the milieu is restricted and there is a reasonable chance for many to follow Shaw's dictum and re-shape it. In checking this out, there appears to be an oscillation with the odd-numbered arenas permitting re-shaping, and the even-numbered arenas resisting re-shaping.
Originally posted: 26-Jan-2026. Last amended: 28-Feb-202
