Different Thinking Styles

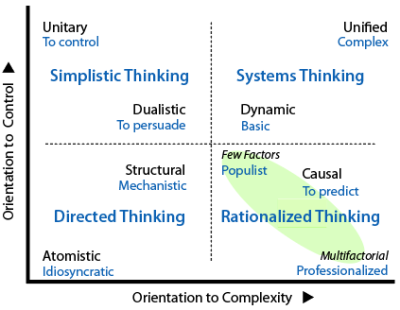
The previous topic examined paradigm preferences for action or ideas guide change. These differences, which are most marked by comparing the diagonals (see diagram at right), contribute to generating distinctive styles of thinking.
Thinking styles vary according to the quadrant. Antagonism naturally develops between protagonists using different styles, most evidently (but not only) between diagonally-opposite quadrants.
Perceptions and accusations of «wrong thinking» can make discussion almost impossible amongst diverse protagonists.
These thinking styles are not proposed as an expression of personal identity, or necessarily used for decision or inquiry. They are thinking tendencies that appear to be secondary, a function of the choice of depiction paradigm, and used to operate change within it.
Simplistic v Rational Thinking
In the UL quadrant, the two paradigms support simplistic thinking because action is regarded as primary and ideas are viewed sceptically and used to manipulate.
In the , almost anything can be asserted because independent thinking is blocked, lying is normalized, and all are expected to conform to a given viewpoint however false or fatuous.
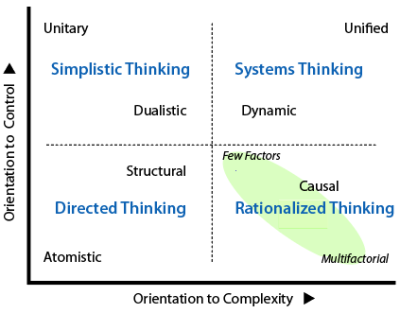
In the , the polarization is generally obvious to all, and convenient or self-serving for the user. Despite appearances or claims to the contrary, comparatively little effort goes into thinking through an issue because most effort goes into generating emotion, winning arguments, and persuading supporters.
In the LR quadrant, the is very different and requires rationalized thinking.
The view is that situations are complicated with many components, and information and theories must be used constructively to find cause-effect relationships. A rational-style of thinking uses evidence and reasoning to propose causation with some confidence. However, so much is ignored that it is best to describe this thinking as rationalized: i.e. made to look rational. Scientific-looking methods may be applied to exclude random associations and handle confounding factors.
: Where a social consensus is necessary thinking focuses on a few core factors and connexions on which all are likely to agree and becomes populist.
: If serious research is pursued, many more factors are recognized as relevant, statistics are introduced. With this degree of complexity, thinking becomes professionalized.
Rationalized thinking fails because it treats human and other factors as able to be ignored or covered by phrases like "everything else being equal" or "a reasonable person". Simple unjustified extrapolation is the norm. Rationalists, especially populists, regularly generate scares of disaster or encourage unwise complacency in this way. However, the future, especially over the longer term, never unfolds along predictable lines.
There is considerable thought control in findings which are typically based on consensus (herd) thinking—both amongst the general populace and within the academic community.
Systems v Directed Thinking
Evolutionary paradigms in the UR quadrant deal with much greater complexity than adherents to other paradigms are willing to address.
In the UR quadrant, both the and require systems thinking because they focus on entities that are assumed to be dynamic systems.
Situations and entities here are always compound with feedback amongst components that are often on different non-linear evolutionary trajectories. System modelling typically requires hierarchies and dualities. reveals basic or standard systems thinking. requires complex systems thinking, commonly referred to as "theories of complexity".
In the LL quadrant, and reduce complexity and simplify control greatly by applying directed thinking, so-called because it is linear, channeled and focused.
The paradigm uses a machine-like model to specify relevant ordering, choice points, roles or responsibilities amongst the components of a particular entity. This directed style is mechanistic and allows for repetition of the form and stable equilibria. Typical results might be a flowchart, process diagram, organizational chart or decision tree.
Depiction using the paradigm acknowledges autonomy and distinctiveness for goal-seeking. Habitual ways of thinking are common. While there may be use of standard practices, this directed style is ultimately idiosyncratic.
Because highly intelligent people can function in any quadrant, the paradigm determines their choices and Intelligence is recruited to serve the paradigm.
That is why after the disaster that follows standard thinking, people ask "what were they thinking?". It is why many often feel that they could do a far better job than the highly paid politicians and bureaucrats who regularly oversee social fiascos, policy disasters and project catastrophes—without ever suffering consequences themselves.
Now that the how and where of change has been considered and the nature of thinking is appreciated, we can focus on how the inevitable mistakes and failures are dealt with by the various paradigms.
- Handling mistakes and failures.
Originally posted: 30-Jun-2024. Last amended: 15-July-2025.
