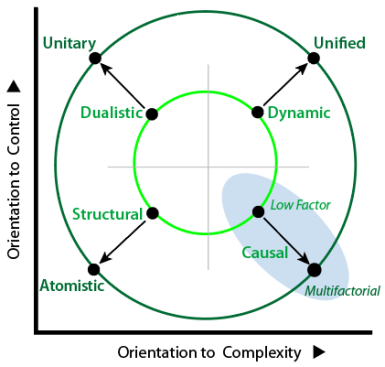
Preview Paradigm Comparisons
Method of Investigation
Appreciation of anything requires comparison with other similar things. In the case of Types, a valuable form of comparison used in THEE is obtained by plotting on the Typology Essentials Table (TET).
In this case, the approach duality, as defined by paradigms along the two diagonals, turned out to be highly revealing: one set of paradigms emerges spontaneously and gives meaning; while the other set requires deliberate effort and organized thought.
A summary of the findings purely in terms of the diagonals is provided below. The goal here is to indicate the sort of findings and thinking that will follow, and not to explain or justify them.
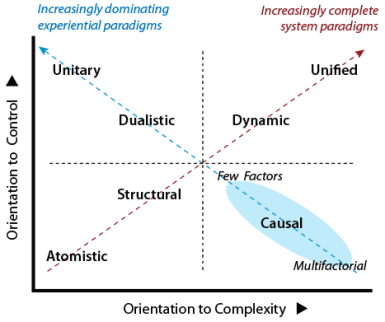
The Approach Duality
 Attitude to Change
Attitude to Change
 Locus of Change
Locus of Change
 Delivering Change
Delivering Change
 Identity Struggles
Identity Struggles
Handling Extremes
 Auspices
Auspices
The Quintessential Depiction Role
Because change commonly involves groups and the change required is either unwanted, baffling, unpleasant, dangerous, or risky for many or most members or the group as a whole, there is a need for a leader to drive change. Change is driven by depiction of the situation.
The role of leader characterizes control in : it can be compared to researcher (for ) or manager (for ).
The nature of this essential psychosocial role differs according to the . Because leadership differs, so does followership.
Leadership of society is a particular challenge. It needs more than a person to handle a society's requirements for change. Political leaders need to espouse and be backed up by a political ideology widely accepted within their society. Each of the appears to align with a particular ideology.
The general pattern for Principal Typologies on the TET, essential to create the Spiral via modes, is as shown in the diagram below.

Using this diagram and the positions of paradigms in the diagram at the top of the page, it is possible to determine the correct taxonomic order and assign each Type of depiction a number. See detailed analysis.
The order in terms of complexity was presented here. So the taxonomic and the complexity orders can now be compared as in the table below. The only commonality is in the 3rd level in both cases.
| Taxonomic Order | Complexity Order | |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | Unitary | Unified |
| 6 | Structural | Atomistic |
| 5 | Unified | Dynamic |
| 4 | Dualistic | Structural |
| 3 | Causal | Causal |
| 2 | Atomistic | Dualistic |
| 1 | Dynamic | Unitary |
Now proceed to work through the above findings for the in detail.
The section ends with a review and some additional analyses supporting the findings and raising questions about the human condition and its handling of reality.
- Start by determining the taxonomic order.
Originally posted: 30-Jun-2024. Last amended: 15-Jul-2025.