Summary: Approaches via the TET
TET Generation
The (syn. psychosocial systems, ) enabling can be plotted against two axes reflecting dimensions of social evolution:
- the inner world of self-development (personal growth), and
- external demands for contributions to society (social growth).
This diagram is called a Typology Essences Table = TET. The axes are the executing duality.
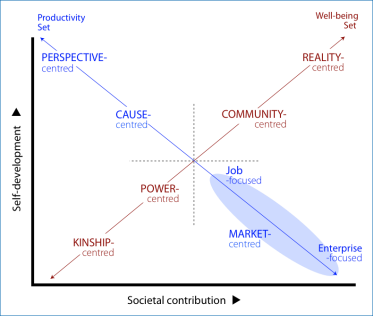
Three lie at extremes, i.e. very high or very low on these axes: kinship-, & reality-centredness. Three approaches lie closer to the centre of the chart: , power- & community-centredness. The centred extends as a diffuse ellipse in the lower-right quadrant with a central form (job-focus) and an extreme form (enterprise-focus) at the ends of the ellipse. Read more
The fall along two diagonal lines, each of which defines a set of meeting a fundamental need of both individuals and society: this is the approach duality. The lying along the line moving from top-left to bottom-right generate worthwhile products in society—the «».
However, sustained productivity requires that demoralisation is kept at bay. The lying along the line moving from bottom-left to top-right stabilize personal well-being—the «well-being set». These can support drive and maintain morale in the face of inevitable setbacks, disappointments and misfortune. They also provide markets with their values.
- contain incompatible assumptions that interfere with holding them all simultaneously. The least incompatibility is to be found between sharing the same quadrant. Read more.
- Outright intolerance and mutual incomprehension exist between in diagonally-opposite quadrants. Read more.
- The location of the in the TET has implications for personal choice. Most people use two , with one being primary. A rationale for choice of is explained here.
- The quadrants show sharply different orientations to money and work. Read more.
- The explain ways that commerce often gets damaged, inadvertently or deliberately. Read more.
- Work exists outside the commercial arena: see the categorization here.
- The provide a useful way to think of incentivization and control of staff that is relevant and sensible in large organizations. Read more.
TET Features
■ Autonomy & Protection
Each person has two primary preoccupations when interacting with others: autonomy (the sense and practice of freedom of action) and protection (the sense and the reality of safety from harm).
-
The diagonal set gives greater value to autonomy,
whereas
- the well-being diagonal set gives greater value to self-protection.
■ Production & Cohesion
Every society has two primary preoccupations affected by interactions among its members: production (the creation of social goods—material, organizational, conceptual, philosophical and artistic) and cohesion (the solid and peaceful integration of all members).
-
The diagonal set gives greater value to production,
whereas
- the well-being diagonal set gives greater value to cohesion.
■ Choice of Mentality
Everybody has one that is dominant or primary. However, because the two diagonal sets complement each other, people need to identify with a second from the other diagonal.
- As you might expect, the pairs are chosen for a similar orientation to self-development or a similar orientation to social contribution.
See more.
■ Responsibility & Rationality
on the diagonal demand a degree of rationality and responsibility. This burden of logic, purpose, knowledge and accountability leads to various approaches to inherent in any endeavour.
- Moving down the diagonal reveals an increase in the burden of responsibility and a requirement for the increasingly disciplined application of rationality to counter the rising level of risk.
See more.
■ Authority & Stability
on the well-being diagonal offer authority and stability and so provide feelings of safety and equilibrium that enable the operation of rationality and responsibility. Disruption may come from anywhere, so these generally encourage a broad and roving attention span.
- Moving up the diagonal is associated with increasing efforts to adapt to and improve society with increasing credence being given to expressed views of individuals. It reveals increasingly effective control of situations and handling of change.
See more.
■ Risk-Reduction
The two diagonal groups reveal different approaches to reducing risk.
- In the case of the , the aim is to maximize efficiency and effectiveness—this depends on .
-
In the case of the well-being set, the aim is to survive and thrive—which depends on attention to others in the group.
■ Effective Perception
The two diagonal groups reveal differences in perceiving reality effectively.
-
The well-being set must be psychologically focused—this requires subjectivity and responsiveness,
while
-
the must be focused on an external and impersonal world—this requires .
Originally posted: July 2009
